Earnings and EPS: Everything Investors Need to Know

The investing information provided on this page is for educational purposes only. NerdWallet, Inc. does not offer advisory or brokerage services, nor does it recommend or advise investors to buy or sell particular stocks, securities or other investments. NerdWallet, Inc. is an independent publisher and comparison service, not an investment advisor. Its articles, interactive tools and other content are provided to you for free, as self-help tools and for informational purposes only.
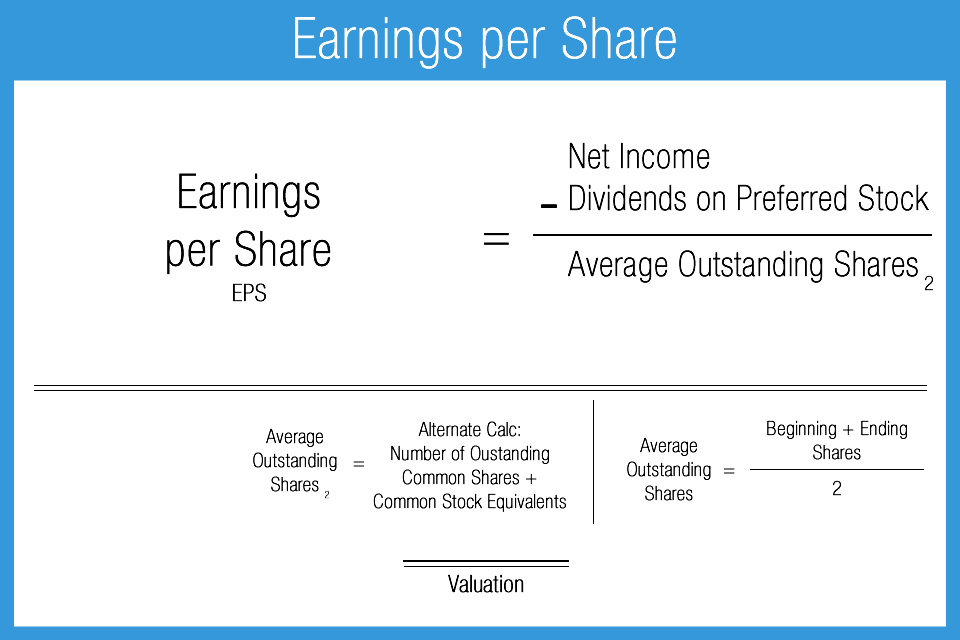
Number of Outstanding Shares
However, the expectations set by analysts also play a role in determining the impact of EPS on the stock price. If a company reports solid EPS growth but falls short of analysts’ expectations, it may lead to the stock price remaining stagnant or even declining in the short term. With EPS and the P/E ratio, investors have an easy way to compare companies, letting them quickly judge the profit represented by each share of stock and how much they’re paying for it. Real estate investment trusts (REITs), which are also popular among dividend investors, are required by law to pay out at least 90% of their taxable income as dividends. They get special tax breaks that help make higher payout ratios more sustainable.
- If a company repurchases shares, its share count will decline, which reduces basic share count during that period.
- Diluted EPS also accounts for other kinds of securities that can be converted into common shares, such as employee stock options and convertible bonds.
- At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
- The accounting rules applied to diluted shares aim to prevent that outcome.
- To calculate a company’s EPS, the balance sheet and income statement are used to find the period-end number of common shares, dividends paid on preferred stock (if any), and the net income or earnings.
- In other words, if a company is currently trading at a P/E of 20x that would mean an investor is willing to pay $20 for $1 of current earnings.
Understanding Basic Earnings Per Share
If a company can quickly grow its EPS, then its stock will likely rise. Short-term growth investors and speculators are particularly interested in companies whose EPS they think will beat analyst estimates, as an earnings beat can fuel a short-term rally in a stock’s price. Earnings per share is also important to dividend investors, growth investors and speculators. In the next part of our exercise, we’ll determine our company’s diluted earnings per share (EPS). The section will contain the EPS figures on a basic and diluted basis, as well as the share counts used to compute the EPS.
What is a good EPS?
Of course, there are no guarantees that the company will fulfill investors’ current expectations. Growth investors typically compare a company’s current EPS to its EPS in the same quarter last year. They might look for a growth stock whose year-over-year EPS growth is higher than others in its industry, or a company whose EPS is growing faster than its share price.
A portion of the earnings may be distributed as a dividend, but all or a portion of the EPS can be retained by the company. Shareholders, through their representatives on the board of directors, would have to change the portion of EPS that is distributed through dividends to access more of those profits. Basic EPS is calculated by dividing a company’s net income by the number of its outstanding shares. When analysts or investors use earnings per share to make decisions, they are usually looking at either basic or diluted earnings per share. This implies that noncumulative shareholders do not build up over time as cumulative preferred investors pay dividends in arrears.
The P/E ratio is used to assess a stock’s valuation, while EPS evaluates profitability. They have similar limitations, but both have historically been reliable metrics for comparing companies and stocks. For example, many high-growth companies have negative EPS numbers, though this doesn’t mean it’s a “bad” figure. Tesla (TSLA), for example, has long been a popular growth stock but it took 18 years before the company reported a profitable year. This means that each ordinary share (common share) of the company earns $2.80 during the period.
She has performed editing and fact-checking work for several leading finance publications, including The Motley Fool and Passport to Wall Street. The net dilution equals the gross new shares in each tranche less the shares repurchased. The P/E ratio is one of the simplest and most popular ways to value a company, especially when comparing it to industry competitors and benchmarks such as the S&P 500. You can also find the EPS on stock information websites like Stock Analysis by accessing the stock’s page and selecting “Financials.” You can browse by quarter, annual, or trailing.
As a result, some of the data will be based on actual figures and some will be based on projections. Companies may choose to buy back their own shares in the open market to improve EPS. The better EPS results limited liability company llc from the net income being divided up by a fewer number of shares. The treasury stock method (TSM) requires the market share price, which we’ll assume is $40.00 as of the latest market closing date.
There are five types of earnings per share, which are discussed further down. Though, there are specific steps the shareholder must take before converting this type of preferred share to a common one. This implies that preferred shareholders do not have the ability to vote for the board of directors or a corporate policy. In a corporation, there are several kinds of shares, each with its own set of rights.
The earnings per share ratio can be calculated from information taken from the income statement and the statement of financial position. EPS is a key component of the price-to-earnings (P/E) valuation ratio. Divide the share price by EPS and you get a multiple denoting how much we pay for $1 of a company’s profit. In other words, if a company is currently trading at a P/E of 20x that would mean an investor is willing to pay $20 for $1 of current earnings. Comparing EPS in absolute terms may not have much meaning to investors because ordinary shareholders do not have direct access to the earnings.
